KI-LECTROLYTE – Intelligent electrolyte engineering and design for industry using AI-accelerated simulation techniques
The electrolyte is the key link within a battery: it enables ion transport between the electrodes and thus determines the battery’s performance, stability, safety, and lifespan. Even small changes in the electrolyte’s composition or its physical and chemical properties can have a major impact on how a battery functions. New electrolytes can enhance the performance and lifetime of modern batteries, improve their safety, or even open the door to entirely new battery chemistries. This makes batteries more efficient, durable, and cost-effective. However, developing new electrolytes is a complex challenge. A battery contains numerous interacting chemical components, and side reactions that reduce cell performance are almost unavoidable. The vast number of possible components and reaction pathways creates an almost infinite chemical space in which traditional trial-and-error methods quickly reach their limits. Data-driven, model-based development is therefore crucial to identify promising formulations more rapidly and optimize them in a targeted manner. An integrated approach is needed to accelerate development – one that systematically connects experimental data and simulation results to make them useful for electrolyte innovation.
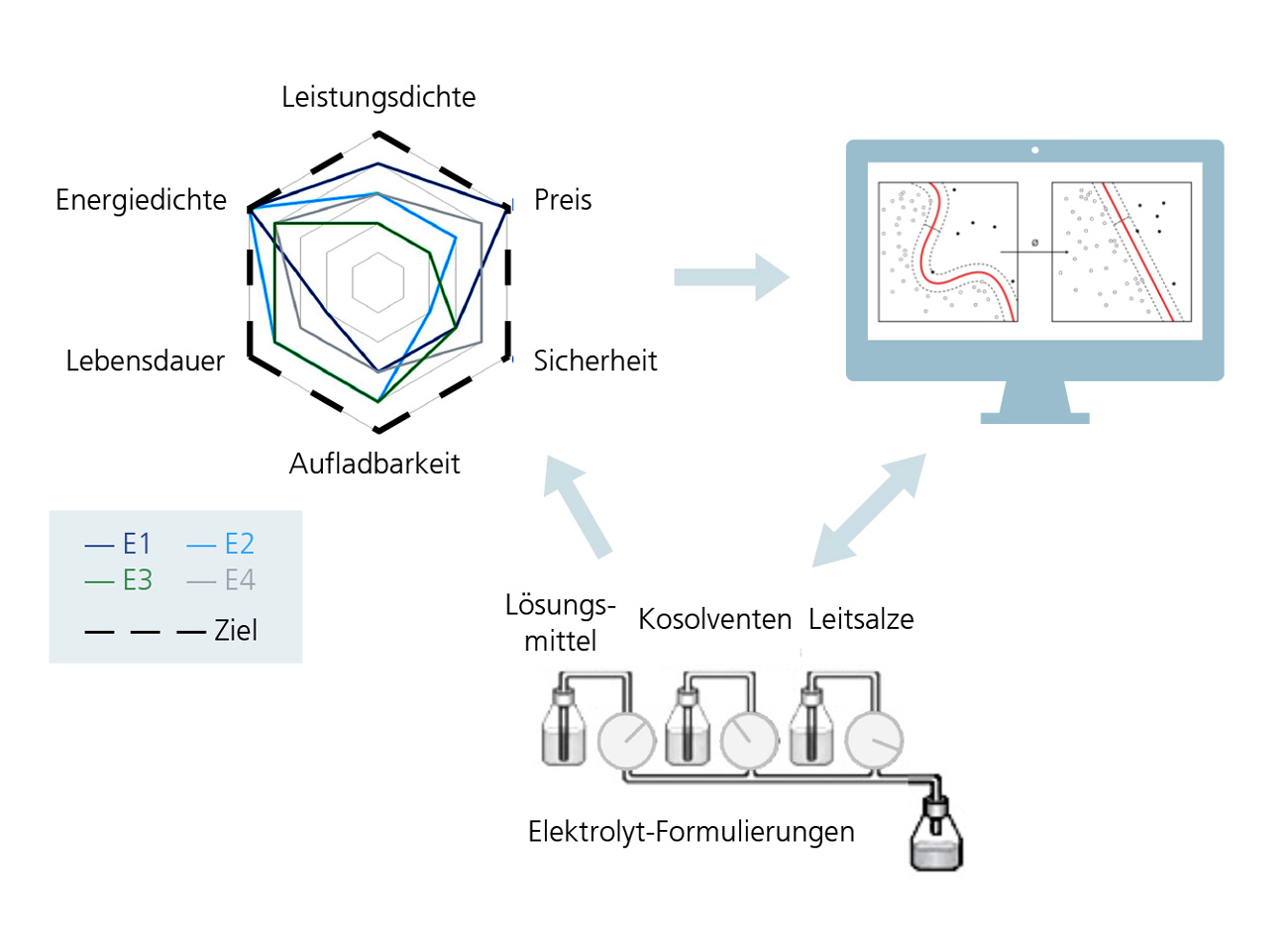
The KI-LECTROLYTE project follows a data- and model-driven approach to discover new electrolyte formulations. The project partners are developing simulation and prediction models to identify electrolyte properties more efficiently. At the heart of the project lies a central electrolyte database that combines experimental data, simulated results, and AI-generated predictions of key material properties. This consolidated database provides high-quality, curated data that support the targeted planning and evaluation of experiments and simulations. The database can be searched specifically for various battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, sodium-ion, or lithium-sulfur batteries. Using this resource, AI-assisted models can accurately predict electrolyte behavior and propose new formulations to optimize existing systems and explore entirely new chemical concepts. By doing so, KI-LECTROLYTE closes an important gap in electrolyte materials research, since structured and comprehensive databases dedicated to electrolytes are still largely missing.
Fraunhofer SCAI contributes its extensive expertise in AI-driven materials science, data integration, and knowledge-based modeling. SCAI develops AI models that reliably predict electrolyte properties, drawing on its experience in atomistic simulation. It also designs the data structure of the new electrolyte database, building on years of expertise in battery ontologies. In addition, SCAI develops general AI models for key battery performance indicators (KPIs) and employs cutting-edge transformer architectures and the generative AI tool LLamol to design novel electrolyte molecules.
KI-LECTROLYTE is funded through the Next.In.NRW program by the Innovationsförderagentur NRW (grant agreement no. EFRE-20801094) of the state North Rhine-Westphalia.
Project duration: 08/2025 until 07/2028

