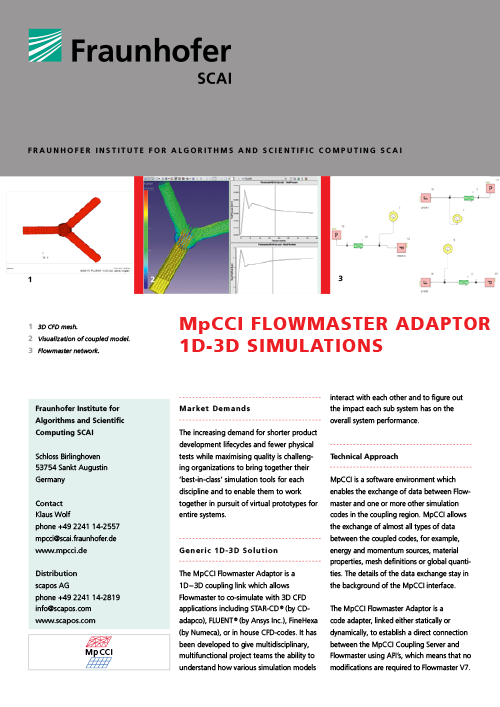
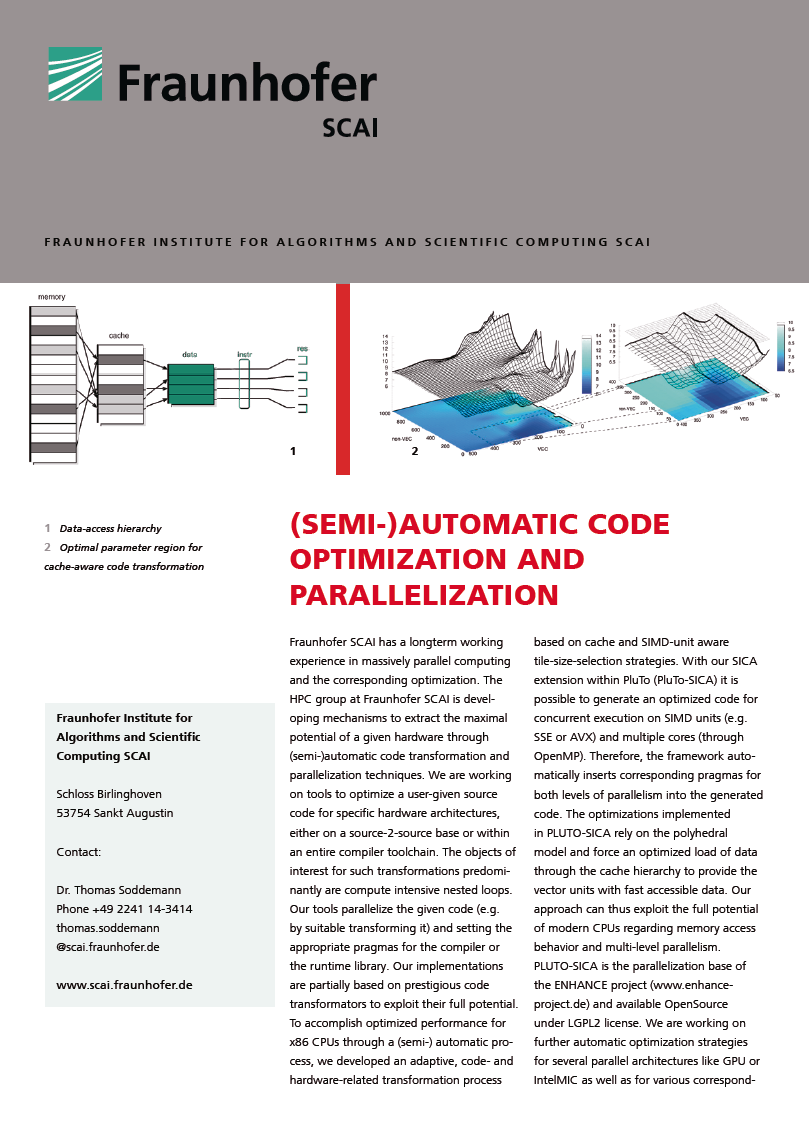
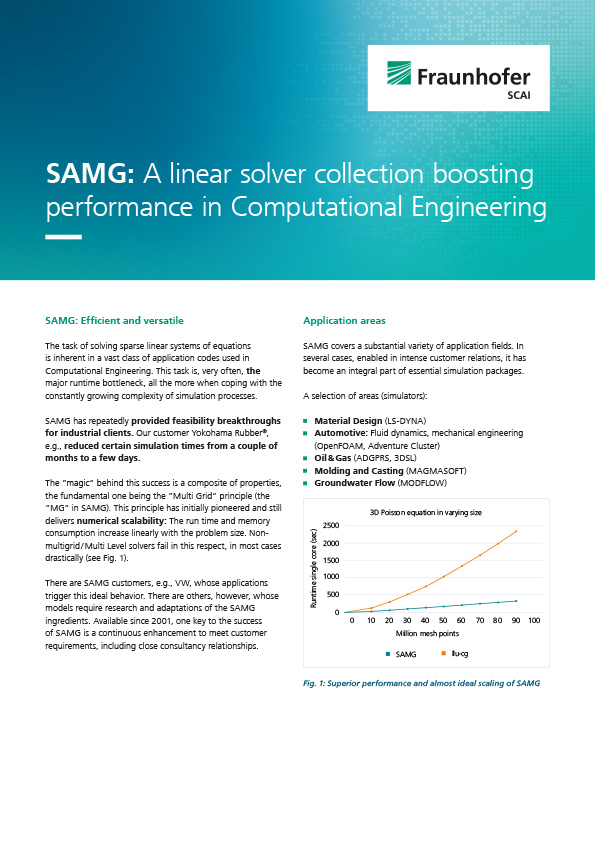
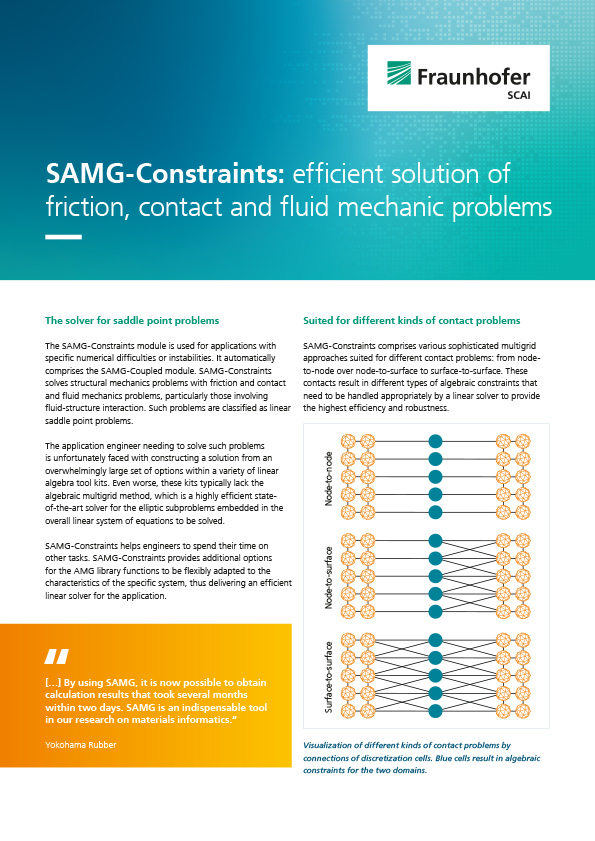
Multiphysics

Coupling Environment
The »MpCCI CouplingEnvironment« has been developed at Fraunhofer SCAI in order to provide an application independent interface for the coupling of different simulation codes. MpCCI CouplingEnvironment has been accepted as a »de facto« neutral standard for simulation code coupling.
Download MpCCI_CouplingEnvironment [PDF, 1,1 MB]